Electrum wallet location of spleen
20 comments
Dogecoin wallet no block source available scholarships
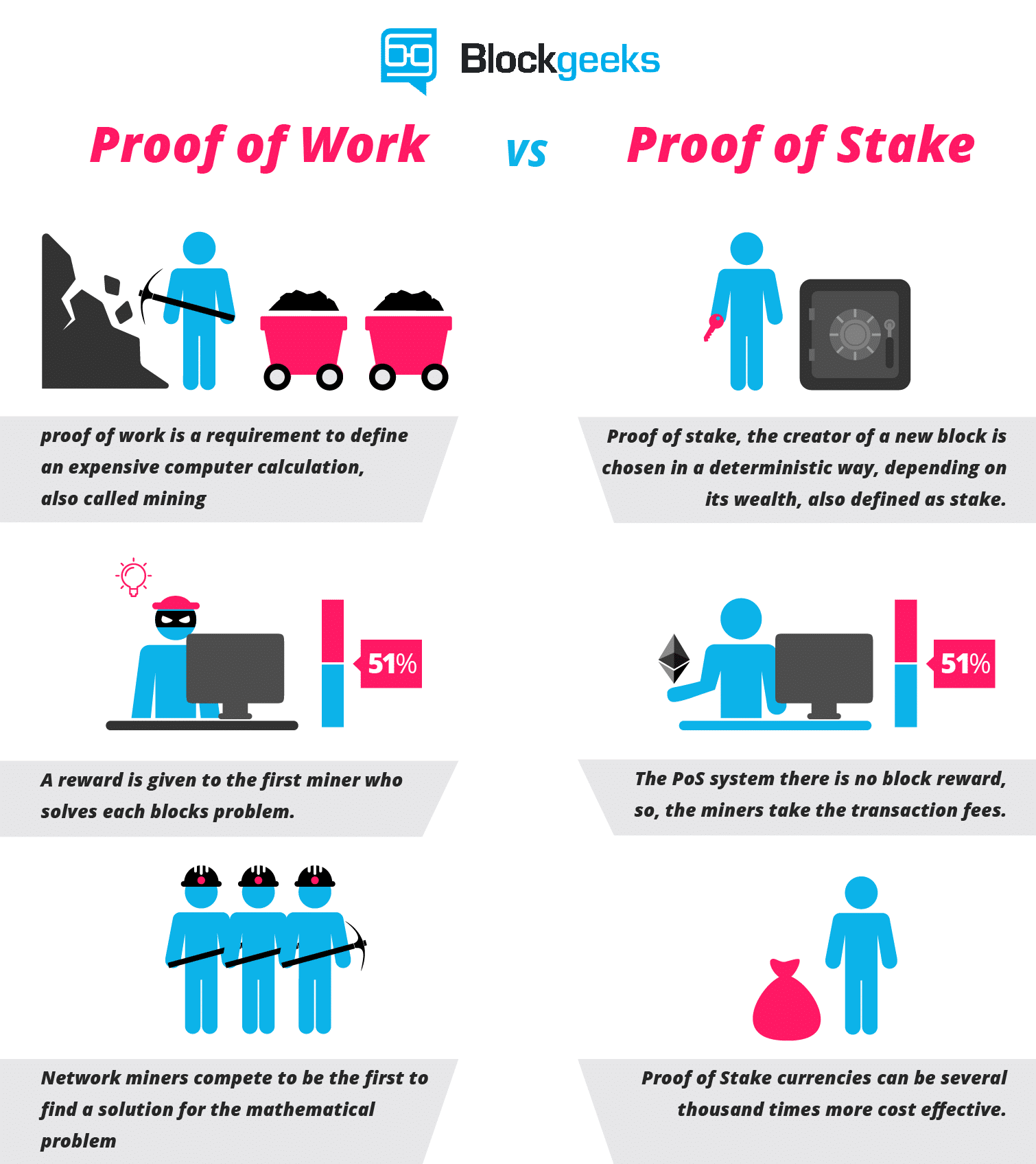
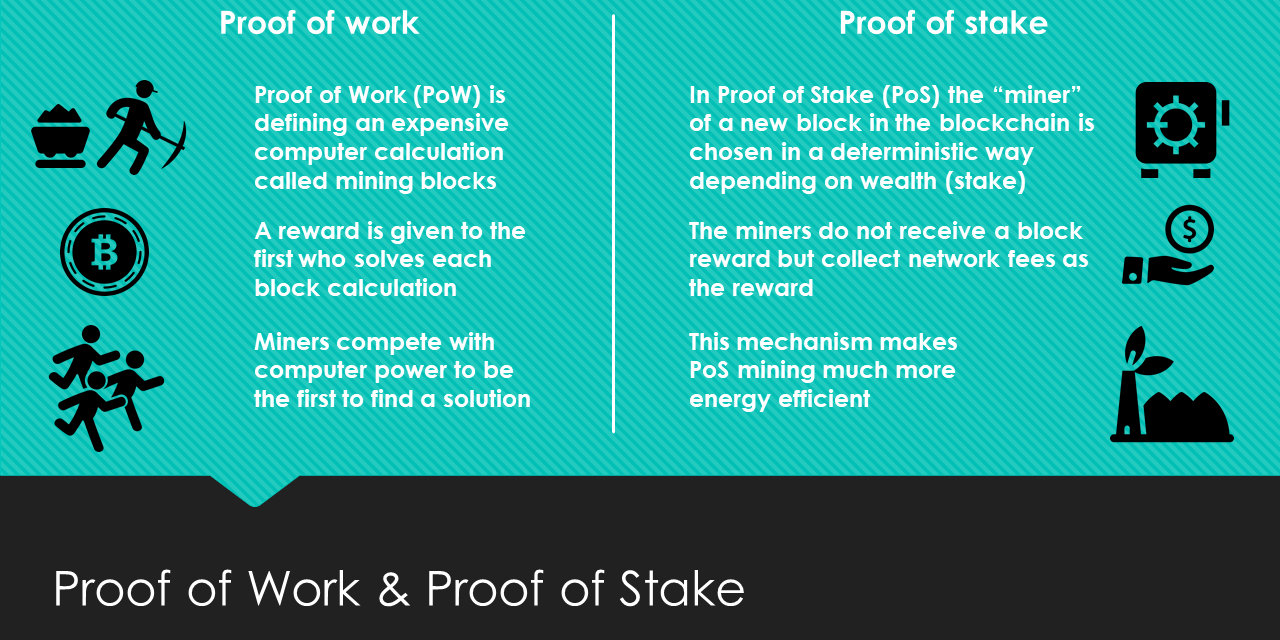
Proof of stake PoS is a type of algorithm by which a cryptocurrency blockchain network aims to achieve distributed consensus. In PoS-based cryptocurrencies, the creator of the next block is chosen via various combinations of random selection and wealth or age i.
In contrast, the algorithm of proof-of-work -based cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin uses mining ; that is, the solving of computationally intensive puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. Proof of stake must have a way of defining the next valid block in any blockchain. Selection by account balance would result in undesirable centralization, as the single richest member would have a permanent advantage. Instead, several different methods of selection have been devised.
Nxt and BlackCoin use randomization to predict the following generator by using a formula that looks for the lowest hash value in combination with the size of the stake. Peercoin 's proof-of-stake system combines randomization with the concept of "coin age", a number derived from the product of the number of coins multiplied by the number of days the coins have been held. Coins that have been unspent for at least 30 days begin competing for the next block.
Older and larger sets of coins have a greater probability of signing the next block. However, once a stake of coins has been used to sign a block, it must start over with zero "coin age" and thus wait at least 30 more days before signing another block. Also, the probability of finding the next block reaches a maximum after 90 days in order to prevent very old or very large collections of stakes from dominating the blockchain.
This process secures the network and gradually produces new coins over time without consuming significant computational power. Another form of staking is running a masternode , [9] a form of decentralized server.
The main disadvantage of operating a masternode is the relatively high barrier to entry as opposed to staking alone. In order to secure the network, those willing to run a masternode are required to purchase a certain number of coins as collateral at current market price. Some coins, such as Dash , have a set cost for a masternode, while other currencies like Divi offer a multitiered system of awards.
Proof-of-stake currencies can be more energy efficient than currencies based on proof-of-work algorithms. Incentives also differ between the two systems of block generation. Under proof of work, miners may potentially own none of the currency they are mining and thus seek only to maximize their own profits. It is unclear whether this disparity lowers or raises security risks.
Some authors [14] [15] argue that proof of stake is not an ideal option for a distributed consensus protocol. One issue that can arise is the "nothing-at-stake" problem, wherein block generators have nothing to lose by voting for multiple blockchain histories, thereby preventing consensus from being achieved. Because unlike in proof-of-work systems, there is little cost to working on several chains, anyone can abuse this vulnerability by attempting to double spend "for free".
Statistical simulations have shown that simultaneous forging on several chains is possible, even profitable. But proof of stake advocates believe that most described attack scenarios are impossible or so unpredictable as to be only theoretical.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject , potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral.
Please help improve it by replacing them with more appropriate citations to reliable, independent, third-party sources. August Learn how and when to remove this template message. Archived from the original on 3 February Retrieved 2 January Retrieved 22 December Retrieved 29 December CoinSutra - Bitcoin Community.
An Introduction and Guide". Retrieved 21 December Retrieved 3 January A Punitive Proof-of-Stake Algorithm". Retrieved 23 January Ethash is the planned PoW algorithm for Ethereum 1. Retrieved Jan 19, Cryptocurrencies without Proof of Work.
Retrieved 30 December Ethereum Ethereum Classic KodakCoin. Dogecoin Gulden Litecoin PotCoin. Dash Decred Primecoin Auroracoin. Proof-of-authority Proof-of-space Proof-of-stake Proof-of-work system. Anonymous Internet banking Bitcoin network Complementary currency Crypto-anarchism Cryptocurrency exchange Digital currency Double-spending Electronic money Initial coin offering Airdrop Virtual currency. Retrieved from " https: Articles lacking reliable references from August All articles lacking reliable references All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from January Views Read Edit View history.
This page was last edited on 23 April , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.