Blockchain basics: Introduction to distributed ledgers
5 stars based on
66 reviews
Get to know this game-changing technology and how to start using it. Everyone is watching how blockchain's distributed ledger technology is revolutionizing the way organizations conduct their business transactions. Let's look at how a blockchain network operates, how you can take advantage of it, and how IBM and other companies are collaborating to advance the technology across a spectrum of industries.
First, a blockchain general ledger background is in order. A distributed ledger is a type of database that is shared, replicated, and synchronized among the members of a decentralized network.
The distributed ledger records the transactions, such as the exchange of assets or data, among the participants in the network. Participants blockchain general ledger the network govern and agree by consensus on the updates to the records in the ledger.
No central authority or third-party mediator, such as a financial institution or clearinghouse, is involved. Every record in the distributed ledger has a timestamp and unique cryptographic signature, thus making the blockchain general ledger an auditable, immutable history of all transactions in the network.
In today's connected and integrated blockchain general ledger, economic activity takes place in business networks that span national, geographic, and jurisdictional boundaries. Assets can be tangible and physical, such as cars, homes, or strawberries, or intangible and virtual, blockchain general ledger as deeds, patents, and stock certificates. Asset ownership and transfers are blockchain general ledger transactions that create value in a business network.
Transactions typically involve various participants like buyers, sellers, and intermediaries such as banks, auditors, or notaries whose business agreements and contracts are recorded in ledgers. A business typically uses multiple ledgers to keep track of asset ownership and asset transfers between participants in its various blockchain general ledger of businesses. Ledgers are the systems of record for a business's economic activities and interests.
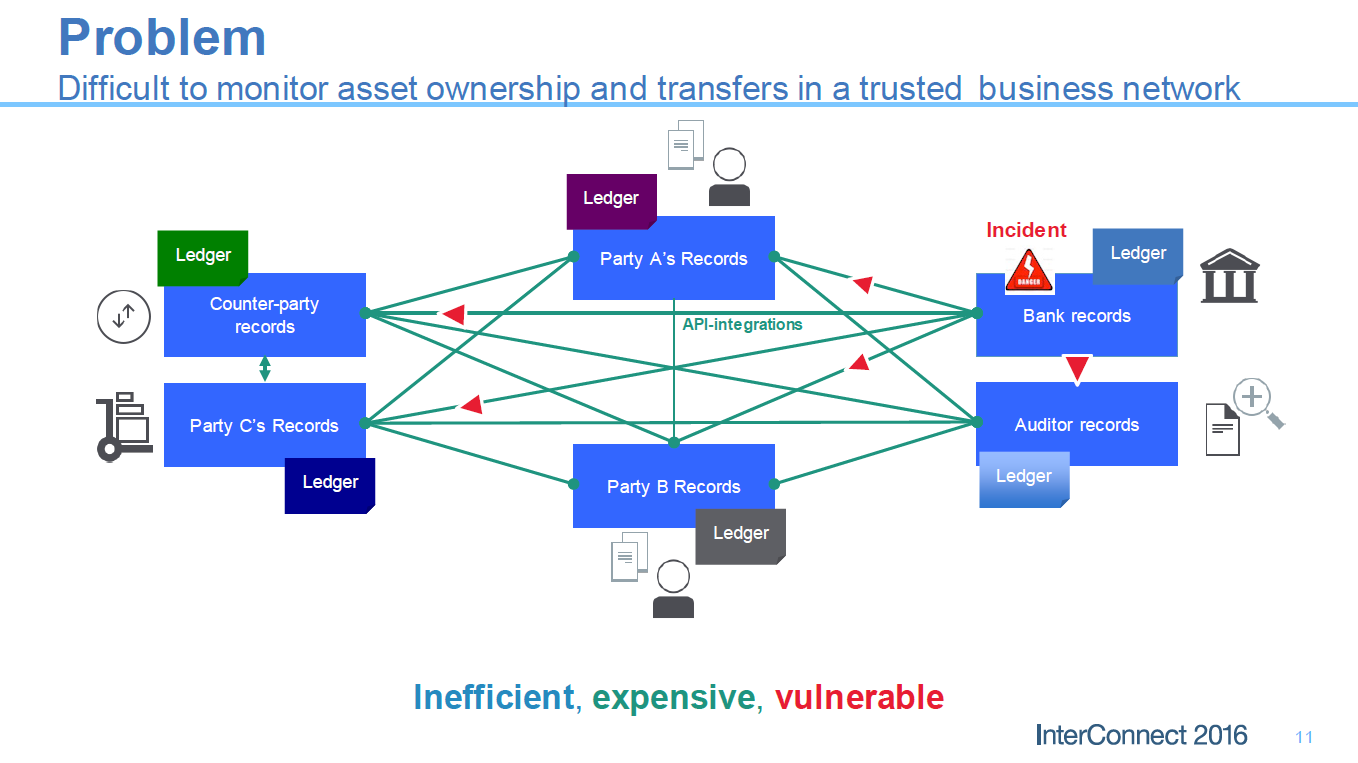
View image at full size. Current business ledgers in use today are deficient in many ways. They are inefficient, costly, and subject to misuse and tampering. Lack of transparency, as well as susceptibility to corruption and fraud, lead to disputes.
Having to resolve disputes and possibly reverse transactions blockchain general ledger provide insurance for transactions is costly. These risks and uncertainties contribute to missed business opportunities. At best, the ability to make a fully informed decision is delayed while differing copies of the ledgers are reconciled.
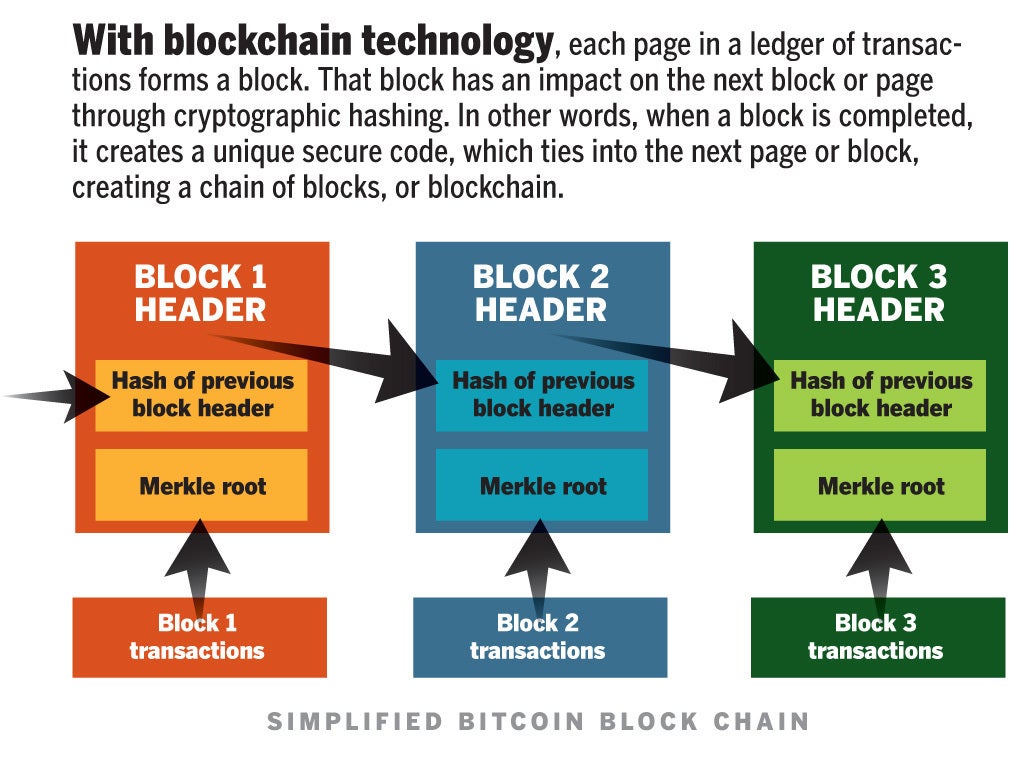
If you hesitated, you're not blockchain general ledger Our Blockchain primer really breaks it down. Read it and you'll be ready to regale your family, neighbors, and co-workers with your new-found fluency! A blockchain is a tamper-evident, shared digital ledger that records transactions in a public or private peer-to-peer network. Distributed to all member nodes in the network, the ledger permanently records, in a sequential chain of cryptographic hash-linked blocksthe history of asset exchanges that take place between the peers in the network.
All the confirmed and validated transaction blocks are linked and chained from the beginning of the chain to the most current block, hence the name blockchain.
The blockchain thus acts as a single source of truth, and members in a blockchain network can view only those transactions that are relevant to them. Take the Blockchain essentials course for developersand you'll learn the ins and outs of asset transfers.
At the end of the free, self-paced course, take a quiz, get a badge, and start planning useful blockchain applications for your business network. Instead of relying on a third party, such as a financial institution, to blockchain general ledger transactions, member nodes in a blockchain network use a consensus protocol to agree on ledger content, and cryptographic hashes and digital signatures to ensure the integrity of transactions.
Consensus ensures that the shared ledgers are exact copies, and lowers the risk of fraudulent transactions, because tampering would have to occur across many places at exactly the same time. Cryptographic hashessuch as the SHA computational algorithm, ensure that any alteration to transaction input — even the most minuscule change — results in a different hash value being computed, which indicates potentially compromised transaction input.
Digital signatures ensure that transactions originated from senders signed with private keys and not imposters. The decentralized peer-to-peer blockchain network prevents any single participant or group of participants from controlling the underlying infrastructure or undermining the entire system. Participants in the network are all equal, adhering to the same protocols. They can be individuals, state actors, organizations, or a combination of all these types of participants.
At its core, the system blockchain general ledger the chronological order of transactions with all nodes agreeing to the validity of transactions using the chosen consensus model.
The result is transactions that cannot be altered or reversed, unless the change is agreed to by all members in the network in a subsequent transaction. Get a monthly roundup of the best free tools, training, blockchain general ledger community resources to put Blockchain to work.
In legacy business networks, all participants maintain their own ledgers with duplication and discrepancies that result in disputes, increased settlement times, and the need for intermediaries with their associated overhead costs.
However, by using blockchain-based shared ledgers, where transactions cannot be altered once validated by consensus and written to the ledger, businesses can save time and costs while reducing risks.
Blockchain consensus mechanisms provide the benefits of a consolidated, consistent dataset blockchain general ledger reduced errors, near-real-time reference data, and the flexibility for participants to change the descriptions of the assets they own. Because no one participating member blockchain general ledger the source of origin for information contained in the shared ledger, blockchain technologies lead to increased trust and integrity in the flow of transaction information among the participating blockchain general ledger.
Immutability mechanisms of blockchain technologies lead to lowered cost of audit and regulatory compliance with improved transparency. And because contracts being executed on business networks using blockchain technologies are automated and final, businesses benefit from increased speed of execution, reduced costs, and less risk, all of which enables businesses to build new revenue streams blockchain general ledger interact with clients.
What blockchain general ledger a good blockchain solution? Blockchain was first blockchain general ledger to the market as the technology underpinning Bitcoin exchangesbut its practical uses in the world of business extend far beyond cryptocurrency transactions. For example, in finance, blockchain networks allow securities trades to be settled in minutes rather than days. In blockchain general ledger chains, blockchain networks allow the flow of goods and payments to be tracked and logged in real time.
To determine whether your use case is a good fit for blockchain, ask yourself these questions:. If you answered yes to the first question and to at least one other, then your use case would benefit from blockchain technology. A network always needs to be involved for blockchain to be the right solution, but the network can take many forms. The network can be between organizationssuch as a supply chain, or the network can be within an organization.
Within an organization, a blockchain network could be used to share reference data between divisions or to create an audit or compliance network, for example. The network can also exist between individualswho might need to store data, digital assets, or contracts on the blockchain, for example.
See industry examples of how diverse organizations — in banking and financial markets, supply chain, healthcare, and transportation, for example — are adopting blockchain to support new business models. Hyperledger is an open source effort to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies for business use. The Hyperledger Fabric framework supports distributed ledger solutions on permissioned networks, where the members are known to each other, for a wide range of industries.
Its modular architecture maximizes the confidentiality, resilience, and flexibility of blockchain solutions. Blockchain general ledger Composer is a set of free, open source tools for quickly prototyping, defining, and testing a Hyperledger Fabric blockchain network and writing applications to interact with it. IBM's point of view blockchain general ledger blockchain technology.
We believe that blockchain is a truly disruptive technology that can transform business networks. We also believe that this innovation has to happen in the open, blockchain general ledger with other technology companies and industries.
To this end, IBM continues to contribute code to several active Hyperledger projects. From IBM's perspective, industrial-grade blockchain technologies have the following characteristics:.
In addition to these attributes, enterprise blockchain technology needs to meet key industry requirements such as performance, verified identifies, and private and confidential transactions. Hyperledger Fabric has been architected to meet these needs. It is also designed with a pluggable consensus model, allowing businesses to select an optimal algorithm for their networks. IBM is the leader in secure open-source blockchain solutions built for the enterprise.
As an early member of the Linux Foundation's Hyperledger Project, IBM is dedicated to supporting the development of openly governed blockchains.
IBM has worked with over clients across financial services, supply chains, IoT, risk management, digital rights management, and healthcare to implement blockchain applications delivered via the IBM Cloud. IBM offers a flexible platform and secure infrastructure to help you develop, govern, and operate your enterprise blockchain network.
Over 40 active networks with multiple organizations are using the IBM Blockchain Platform to exchange assets every day and improve business processes ranging from food safety to trade efficiencies and digital payments. Learn about IBM Blockchain solutionsand see how you can start using blockchain in your business today. If you're a developer, the easiest, most economical way to learn your way around a real business blockchain and start developing blockchain skills and applications now is to sign up for the IBM Blockchain Platform Starter Plan free beta.
With the new Starter Plan, you can quickly spin up a blockchain pre-production network, deploy sample applications, and develop and deploy client applications.
Blockchain technologies represent a fundamentally new way to transact business. They usher in a robust and blockchain general ledger next generation of applications for the registry and exchange of physical, virtual, tangible, and intangible assets. Thanks to the key concepts of cryptographic security, decentralized consensus, and a shared public ledger with its properly controlled and permissioned visibilityblockchain technologies can profoundly change the way we organize our economic, social, political, and scientific activities.
We'll conclude this introduction to distributed ledgers with six great ways to continue your blockchain odyssey:. Sign in or register to add and subscribe to comments. Introduction to distributed ledgers Get to know this game-changing technology and how to start using it Blockchain general ledger Brakeville and Bhargav Perepa Published on March 18, Now, could you explain "blockchain" to someone? Test your blockchain knowledge! Is blockchain is right for you?
Comments Sign in or register to add and subscribe to comments. Subscribe me to blockchain general ledger notifications.