A Non-Architect’s Guide to Blockchain Architecture
4 stars based on
47 reviews
Why is the Blockchain such a terrific innovation? The creation of the Blockchain by the eponymous Satoshi Nakamoto is nothing short of a work of disruptive genius. Banking is a system of intermediaries across the spectrum — ranging from payment networks e. In Banking, large institutions stand behind and protect payment systems. The Blockchain serves that purpose in the realm of the Bitcoin and stands behind every bitcoin ever created by maintaining the proof of ownership.
Prior to Blockchain, two important shortcomings blockchain technical architecture hindered the development of a truly secure digital currency. Lets examine each of these in the context of the current public blockchain in terms of an end to end transaction shown below. It is my expectation blockchain technical architecture other kinds of blockchain variants will leverage the current technology as a foundational design pattern while layering in their own industry or consortium specific requirements.
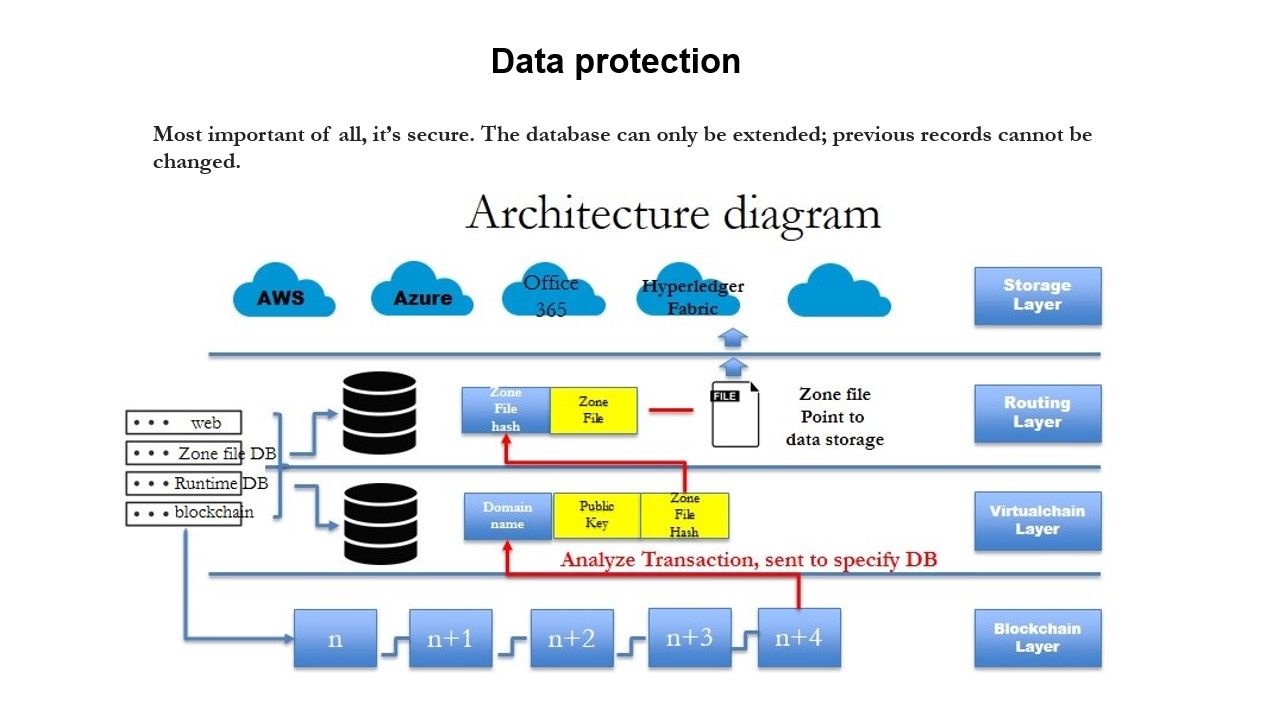
The Blockchain itself blockchain technical architecture an application that runs on a network of distributed servers. The below architecture diagram broadly captures the 3 main layers of the Blockchain along with their roles. Illustration 2 — Blockchain Architectural Layers Click to enlarge. Once installed on a server, the full Blockchain client syncs up with other nodes in the network.
From then onwards the particular blockchain technical architecture maintains all and any transaction records conducted using bitcoins or any other application running on the Blockchain. As stated above, the Blockchain software operates at such a massive scale which makes it virtually impossible and cost prohibitive to hack or otherwise break into bitcoin or any other application running on it.
Thus there is no need for a central 3rd party to a issue, authenticate blockchain technical architecture validate ownership of the currency. The nodes in the overall network blockchain technical architecture the peer-to-peer IP network to process and verify transactions.
When several nodes blockchain technical architecture have the same blocks in their individual databases, they are considered to be in consensus. Blockchain is a peer to peer P2P network working on the IP protocol on the internet.
A P2P network blockchain technical architecture essentially a flat topology with no centralized node, hierarchy, or special server node. Every node blockchain technical architecture a fully replicated copy of a blockchain technical architecture that blockchain technical architecture the payment history of every bitcoin ever created along with ownership information. As transactions happen using the currency, a consensus mechanism essentially dictates how nodes agree on blockchain updates.
The graphic below shows the current number of nodes active in the bitcoin network and their locations on the globe. Illustration 3 — Blockchain Nodes — Jan 25, [4]. Though the blockchain enforces an equal structure among all the nodes that are part of the network, nodes can play different roles based on their flavor or business intention. Full nodes maintain a complete copy blockchain technical architecture the blockchain database and can verify any transaction without the need for an external lookup.
On the other end of the spectrum, nodes that blockchain technical architecture store a subset of the blockchain database verify transactions using a method called Simplified Payment Verification SPV.
Mining also creates an implicit meritocracy in that systems which can process transactions faster blockchain technical architecture more efficiently get credited for them. For applications like bitcoin, rollbacks currently are almost impossible in the vanilla blockchain architecture — which is a current limitation. Once nodes are booted up, they perform a peer discovery to contact any other valid node using a given port over TCP.
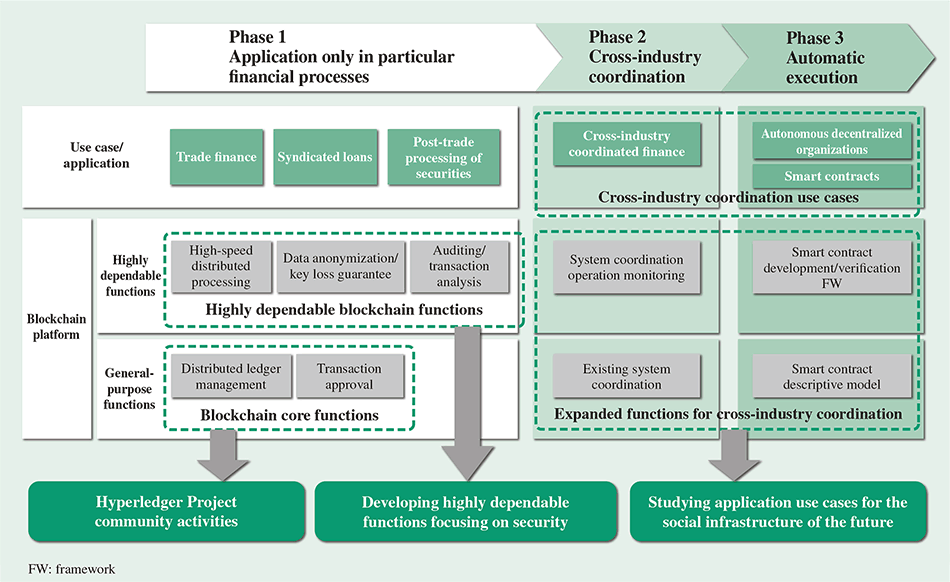
The Blockchain stack is depicted below and is layered on the OSI stack. The Blockchain Message Exchange specifies the handshake logic between nodes as well as the serialization format for messages exchanged over the wire. Developers will essentially use this layer to extend vanilla blockchain to support other kinds of applications which can leverage the existing bitcoin blockchain to validate their transactions.
Other kinds of virtual currency, sidechains etc. The above illustration depicts how currency transactions are converted into blocks.
As can be seen,once a transaction typically a kiosk purchase or wire transfer or credit card payment etc is submitted into the system, a transaction say Transaction A is generated that is pushed into the blockchain node blockchain technical architecture. The generated hash is then stored with other metadata into the header of a data structure called a block.
The header is key blockchain technical architecture it becomes the basis for running the hash function again to create a child block. The hash function is used as the math puzzle that the miners race to solve by looking over virtually trillions of possibilities. The miner that solves it first submits it for a check blockchain technical architecture other nodes and once confirmed, the block is stored into the blockchain for posterity.
The miner node blockchain technical architecture then credited a very small percentage of the transaction as fees. Your email blockchain technical architecture will not be published. Notify me of follow-up comments by email. Notify me of new posts by email. Let us consider Banking as we have known and understood blockchain technical architecture for almost years.
What is different with bitcoin is that once a bitcoin has been purchased or transferred anywhere in the world — blockchain technical architecture is established and recorded authoritatively via the Blockchain. The Blockchain operates at such a massive scale which makes it virtually impossible and cost prohibitive to hack or otherwise break into bitcoin.
Doing these ensures that the Miner node s can mine a block of transactions during the same time. The benefit to the Miners is that they can keep the transaction fees associated with that block as a reward.
It is almost impossible for this system to be broken into as it is in the interest of all the miners to form a distributed consensus based on valid block information. This capability is termed as the proof of work Blockchain Architecture Considerations: Illustration 2 — Blockchain Architectural Layers Click to enlarge Once installed on a server, the full Blockchain client syncs up with other nodes in the network. Nodes in the Blockchain: Illustration 3 — Blockchain Nodes — Jan 25, [4] Though the blockchain enforces an equal structure among all the nodes that are part of the network, nodes can play different roles based on their flavor or business intention.
Salient features of transactions — Transactions can be created on the behalf of any client using a Mobile Wallet or any other client application Transactions contain the actual business data to be stored in the blockchain Blocks record the sequence of transactions in the blockchain. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. The immense potential of the Blockchain technical architecture. How the Blockchain will lead disruption across industry.