Buy liquid nitrogen spray
19 comments
Comprar bitcoin plus500
In a centralized economy, currency is issued by a central bank at a rate that is supposed to match the growth of the amount of goods that are exchanged so that these goods can be traded with stable prices. The monetary base is controlled by a central bank. In the United States, the Fed increases the monetary base by issuing currency, increasing the amount banks have on reserve or by a process called Quantitative Easing.
In a fully decentralized monetary system, there is no central authority that regulates the monetary base. Instead, currency is created by the nodes of a peer-to-peer network. The Bitcoin generation algorithm defines, in advance, how currency will be created and at what rate. Any currency that is generated by a malicious user that does not follow the rules will be rejected by the network and thus is worthless. Bitcoins are created each time a user discovers a new block.
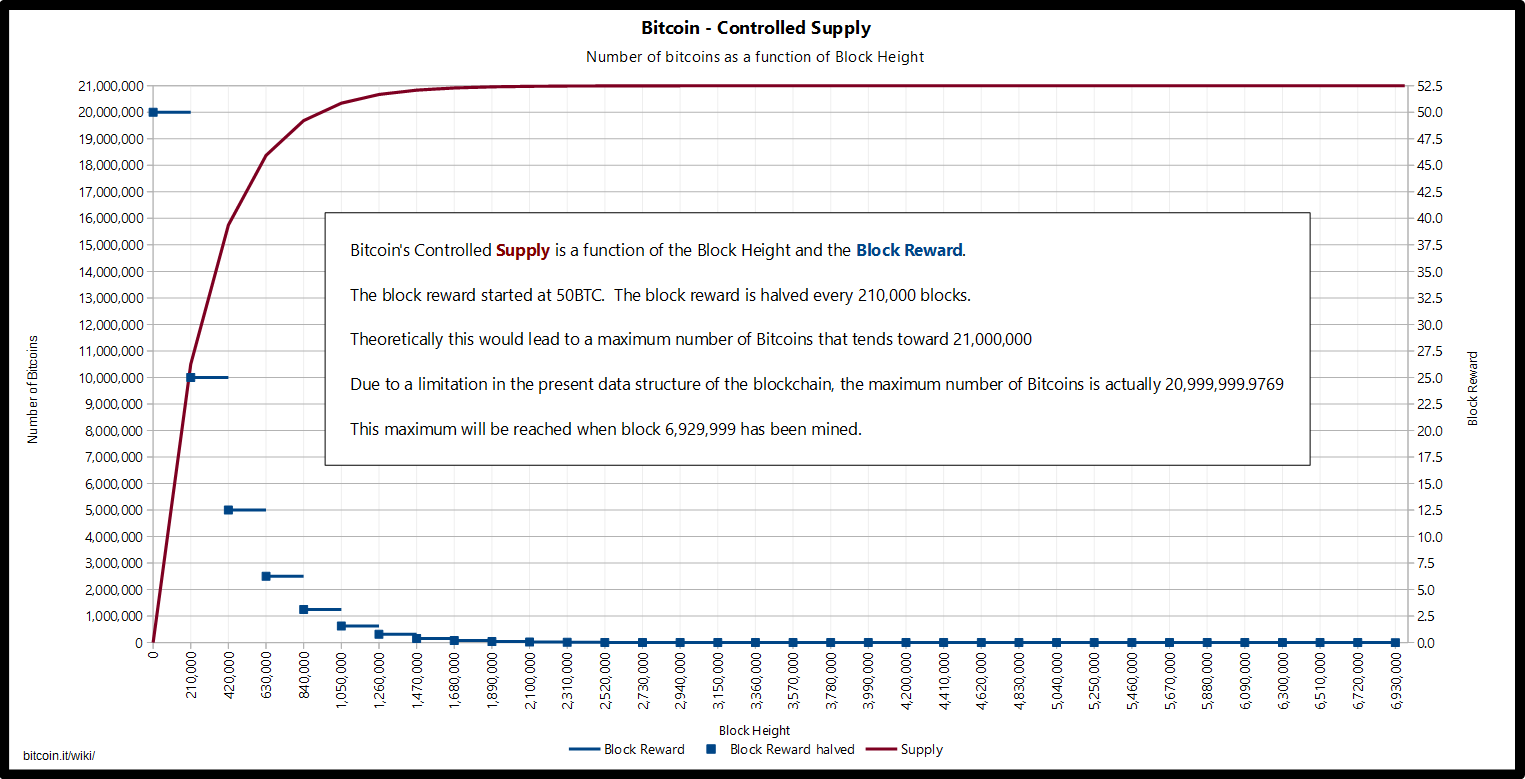
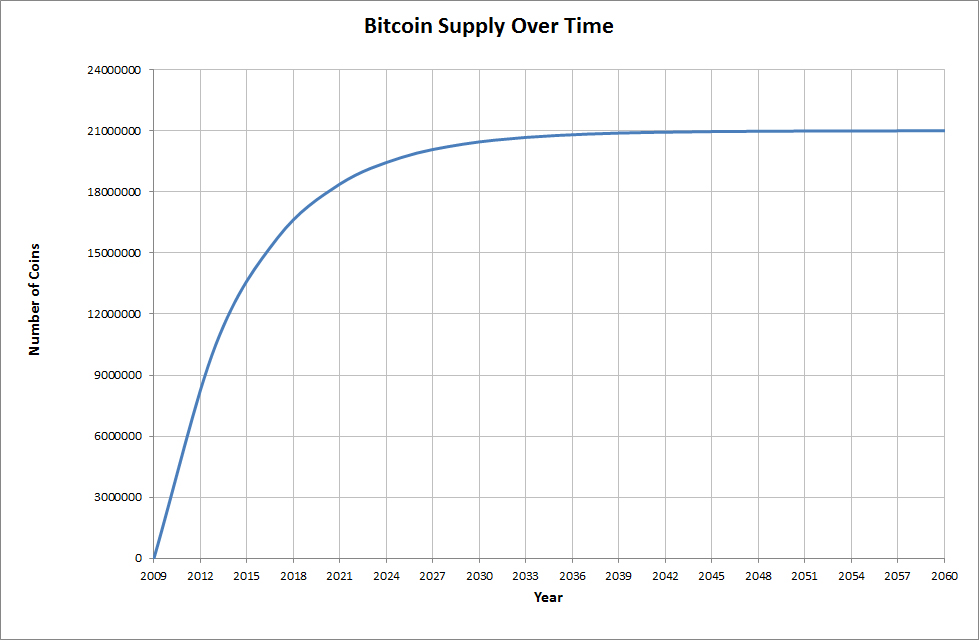
The rate of block creation is adjusted every blocks to aim for a constant two week adjustment period equivalent to 6 per hour. The result is that the number of bitcoins in existence will not exceed slightly less than 21 million. Satoshi has never really justified or explained many of these constants.
This decreasing-supply algorithm was chosen because it approximates the rate at which commodities like gold are mined. Users who use their computers to perform calculations to try and discover a block are thus called Miners. This chart shows the number of bitcoins that will exist in the near future.
The Year is a forecast and may be slightly off. This is one of two only known reductions in the total mined supply of Bitcoin. Therefore, from block onwards, all total supply estimates must technically be reduced by 1 Satoshi. Because the number of bitcoins created each time a user discovers a new block - the block reward - is halved based on a fixed interval of blocks, and the time it takes on average to discover a block can vary based on mining power and the network difficulty , the exact time when the block reward is halved can vary as well.
Consequently, the time the last Bitcoin will be created will also vary, and is subject to speculation based on assumptions. If the mining power had remained constant since the first Bitcoin was mined, the last Bitcoin would have been mined somewhere near October 8th, Due to the mining power having increased overall over time, as of block , - assuming mining power remained constant from that block forward - the last Bitcoin will be mined on May 7th, As it is very difficult to predict how mining power will evolve into the future - i.
The total number of bitcoins, as mentioned earlier, has an asymptote at 21 million, due to a side-effect of the data structure of the blockchain - specifically the integer storage type of the transaction output , this exact value would have been 20,, Should this technical limitation be adjusted by increasing the size of the field, the total number will still only approach a maximum of 21 million. The number of bitcoins are presented in a floating point format.
However, these values are based on the number of satoshi per block originally in integer format to prevent compounding error. Therefore, all calculations from this block onwards must now, to be accurate, include this underpay in total Bitcoins in existence. Then, in an act of sheer stupidity, a more recent miner who failed to implement RSK properly destroyed an entire block reward of The bitcoin inflation rate steadily trends downwards.
The block reward given to miners is made up of newly-created bitcoins plus transaction fees. As inflation goes to zero miners will obtain an income only from transaction fees which will provide an incentive to keep mining to make transactions irreversible.
Due to deep technical reasons, block space is a scarce commodity , getting a transaction mined can be seen as purchasing a portion of it. By analogy, on average every 10 minutes a fixed amount of land is created and no more, people wanting to make transactions bid for parcels of this land.
The sale of this land is what supports the miners even in a zero-inflation regime. The price of this land is set by demand for transactions because the supply is fixed and known and the mining difficulty readjusts around this to keep the average interval at 10 minutes. The theoretical total number of bitcoins, slightly less than 21 million, should not be confused with the total spendable supply. The total spendable supply is always lower than the theoretical total supply, and is subject to accidental loss, willful destruction, and technical peculiarities.
One way to see a part of the destruction of coin is by collecting a sum of all unspent transaction outputs, using a Bitcoin RPC command gettxoutsetinfo. Note however that this does not take into account outputs that are exceedingly unlikely to be spent as is the case in loss and destruction via constructed addresses, for example. The algorithm which decides whether a block is valid only checks to verify whether the total amount of the reward exceeds the reward plus available fees.
Therefore it is possible for a miner to deliberately choose to underpay himself by any value: This is a form of underpay which the reference implementation recognises as impossible to spend. Some of the other types below are not recognised as officially destroying Bitcoins; it is possible for example to spend the 1BitcoinEaterAddressDontSendf59kuE if a corresponding private key is used although this would imply that Bitcoin has been broken.
Bitcoins may be lost if the conditions required to spend them are no longer known. For example, if you made a transaction to an address that requires a private key in order to spend those bitcoins further, had written that private key down on a piece of paper, but that piece of paper was lost. In this case, that bitcoin may also be considered lost, as the odds of randomly finding a matching private key are such that it is generally considered impossible.
Bitcoins may also be willfully 'destroyed' - for example by attaching conditions that make it impossible to spend them. A common method is to send bitcoin to an address that was constructed and only made to pass validity checks, but for which no private key is actually known.
An example of such an address is "1BitcoinEaterAddressDontSendf59kuE", where the last "f59kuE" is text to make the preceding constructed text pass validation.
Finding a matching private key is, again, generally considered impossible. For an example of how difficult this would be, see Vanitygen. Another common method is to send bitcoin in a transaction where the conditions for spending are not just unfathomably unlikely, but literally impossible to meet. A lesser known method is to send bitcoin to an address based on private key that is outside the range of valid ECDSA private keys. The first BTC 50, included in the genesis block , cannot be spent as its transaction is not in the global database.
In older versions of the bitcoin reference code, a miner could make their coinbase transaction block reward have the exact same ID as used in a previous block [3]. This effectively caused the previous block reward to become unspendable. Two known such cases [4] [5] are left as special cases in the code [6] as part of BIP changes that fixed this issue.
These transactions were BTC 50 each. While the number of bitcoins in existence will never exceed slightly less than 21 million, the money supply of bitcoins can exceed 21 million due to Fractional-reserve banking. Because the monetary base of bitcoins cannot be expanded, the currency would be subject to severe deflation if it becomes widely used.
Keynesian economists argue that deflation is bad for an economy because it incentivises individuals and businesses to save money rather than invest in businesses and create jobs. The Austrian school of thought counters this criticism, claiming that as deflation occurs in all stages of production, entrepreneurs who invest benefit from it. As a result, profit ratios tend to stay the same and only their magnitudes change. In other words, in a deflationary environment, goods and services decrease in price, but at the same time the cost for the production of these goods and services tend to decrease proportionally, effectively not affecting profits.
Price deflation encourages an increase in hoarding — hence savings — which in turn tends to lower interest rates and increase the incentive for entrepreneurs to invest in projects of longer term. A fixed money supply, or a supply altered only in accord with objective and calculable criteria, is a necessary condition to a meaningful just price of money.
Retrieved from " https: Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in. Views Read View source View history. Sister projects Essays Source. This page was last edited on 26 April , at Content is available under Creative Commons Attribution 3. Privacy policy About Bitcoin Wiki Disclaimers.