Bitcoin Hash Functions Explained
5 stars based on
49 reviews
How "mining" works is at the very heart of Bitcoin. It is often brushed over and simply referred to as "complicated math" in the mediabut it's actually quite simple to understand even if it is computationally intensive to solve. Most of the content in this post comes from a post on Reddit that I have edited, reformatted, and elaborated on. Feel free to read the original post if you prefer.
Understanding hashes is the bitcoin mining hashes solved step in understanding mining. A hash will take an input of any length, and generate is seemingly randomised output of a specific length. The same input will always generate the same output, but changing just one character will drastically change the output.
For example, af2f0fb8fbb0d2ed1c1cd2a1ec0fb85daa is the hash of hello worldand 30ede9ea08ff1adb8aa6be05fdf84aeacabb5 is the hash of hello worle. This behaviour makes it very difficult to predict what input gives a particular output.
For example, what input gives aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa as a hash? It's effectively impossible to work it out. People will often build lookup tables that map these inputs to outputs in order to perform quick reversals later.
These tables are called rainbow tables and rely on the input already having been hashed. The second step is to get the idea of a proof of work.
It might be impossible to find a hash specifically with a string consisting of nothing but the letter "a" but what if we asked for a hash bitcoin mining hashes solved a single zero at the front? Altering the last letter of hello world took 26 attempts to finally get hello worlC which equates to 0d7eae0fab3abc2cccc0bb4aabb24ffaf8c.
Why is this useful? Because it creates a puzzle whose difficulty is measurable and which it's impossible to perform better than bitcoin mining hashes solved guessing. That second property is important because it's the only bitcoin mining hashes solved to create a fair "mining" system.
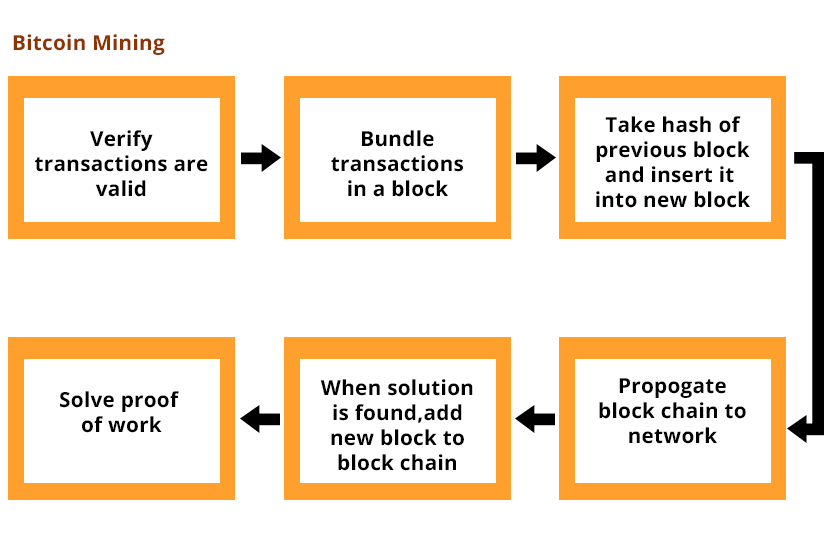
Miners solve such puzzles as above but bitcoin mining hashes solved are far more difficult. For example, find a hash that looks like this: Each hash is can be considered to be just a number.
For example, the hash ab3abc2cccc0bb4aabb24ffaf8c has a numeric value of So in mining, bitcoin mining hashes solved miners have to achieve a hash with a numeric value lower than a specified number. This number is called the target. If your hash attempt gives you a number less than the target, which is the same thing as having a bunch of zeros at the front of the hash, then you win and you get to "mine the block".
To find such a small hash takes millions of attempts, or more accurately, the whole mining network, with everyone trying at bitcoin mining hashes solved same time, needs millions of billions of tries to get it right. The part of the content that they are hashing and bitcoin mining hashes solved allowed to change, a single number, in order to try and get a hash beginning with zeros, is called the nonce.
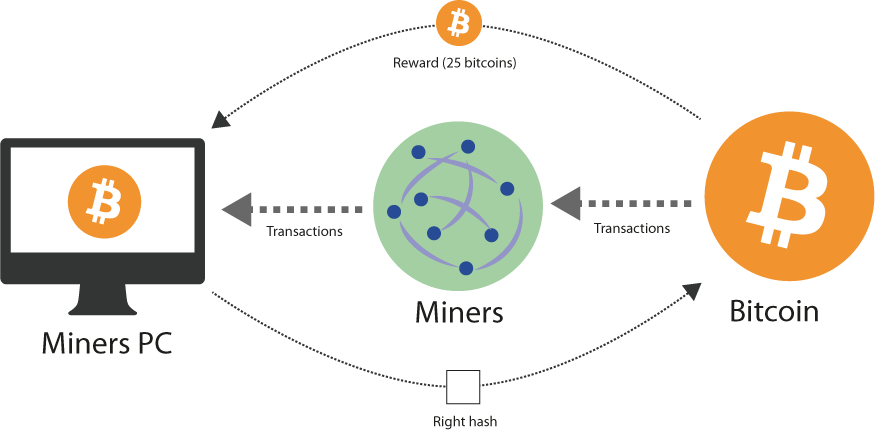
The current block reward of 25 Bitcoins is given to the miner who successfully "mines the block" finds the appropriate hash. It's not really that mining "generates" the Bitcoin in any sense, it's just that it's written into Bitcoin code that a transaction block starts with a unique transaction called a "coinbase" transaction, which is the only type of transaction with no inputs.
It only has an output, consisting of the reward plus the transaction fees. To make any sense of Bitcoin's solution to this problem, bitcoin mining hashes solved need to understand also what is meant by "distributed timestamp server" and how proof of work hashes can be used to construct this.
It is, very briefly, explained in Sections 3 and 4 of the bitcoin whitepaper. You're creating a sequence of blocks, tied to each other by including the hash of the last one in the next one. This proves that the next bitcoin mining hashes solved knew about the last block remember, hashes are totally unpredictablewhich proves that it came afterwards.
However, bitcoin mining hashes solved not enough; you bitcoin mining hashes solved know that block 8 comes after block 7, but what if a different block 8, put in by a different miner, also comes after block 7? Worse still, what if these two competing blocks, 8a and 8b contain different transactions, spending money to different places?
Which one is the "true" block of transactions? The reason miners did the complicated proof of work process above is exactly to solve this problem. In bitcoin, the chain of blocks with the largest total proof of work embedded in it is the "winner". The reason this is such a good way of deciding is that it makes it incredibly difficult for an attacker someone, say, who wants to spend the same Bitcoins twice to create an alternative single block or chain of blocks and try to convince everyone else on the network that theirs is the right one.
Since everyone else is working on the "true" chain, they have an enormous amount of CPU power working together to create it. Lastly, here is Satoshi's explanation of the Byzantine Generals' problem. Hopefully you can see how it connects. The math problem that these mining computers solve serves no purpose other than to secure Bitcoin's network from attackers wishing to "double spend". Miners are not creating a massive rainbow table or computing the human genome.
As more computers are thrown at the problem, and hardware advances, the problem is artificially made more difficult to compensate. This seems incredibly wasteful to bitcoin mining hashes solved as we start to read about the electrical costs of the Bitcoin network and think about the fact that Bitcoin could easily run on just 3 computers to be considered distributed. This is why I have high hopes for alternative cryptocurrencies, such as Peercointhat implement proof-of-stake.
The network could run on bitcoin mining hashes solved devices, such as people's phones and tablets rather than purpose-built and costly ASICs that will be redundant in a few years. Programster's Blog Tutorials focusing on Linux, programming, and open-source.
Bitcoin's Mathematical Problem bitcoin mining. We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.