What Will Blockchain Mean for Banks?
4 stars based on
51 reviews
Blockchain is transforming everything from payments transactions to how money is raised in the private market. As it picks up momentum, will the traditional banking industry embrace this new technology or be replaced by it?
Someone is going to get killed. It is a vehicle to perpetrate fraud. But this very loud and public backlash against cryptocurrencies from banks begs the question: What do banks have to be afraid of?
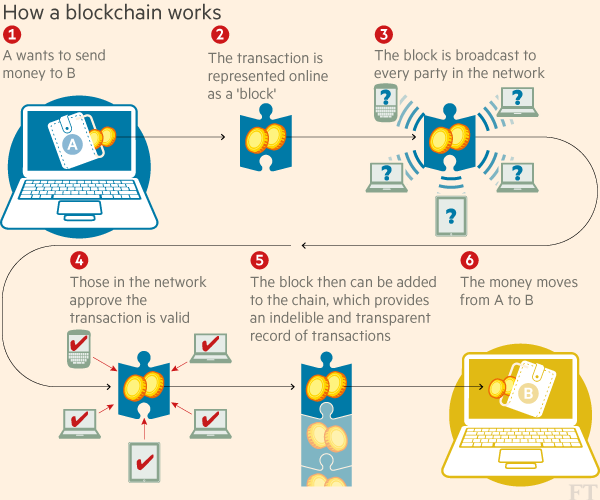
Blockchain technology provides a cryptographically secure way of sending digital assets, without the need for trusted third parties — such as banks.
Further, tools such as smart contracts promise to automate many of the tedious processes within the banking industry, from compliance and claims processing, to distributing the contents of a will. Banks help intermediate payments, make loans, and provide credit. The promise of blockchain as a trustless, disintermediated technology is to disrupt all of that, including:. Today, trillions of dollars slosh around the world via an antiquated system of slow payments and added fees.
The typical cost per transaction for a money sender averages to 7. Facilitating payments is highly profitable for banks, providing them with little incentive to lower fees. A excerpt from a leaked internal Santander document shows revenues from international money transfers, and the risk of disruption.
Blockchain is disrupting this system by offering a higher-security and lower-cost way to send peer-to-peer P2P payments — one that requires no intermediary. Because cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are built around a public, decentralized ledger that anyone can use to send and receive money, it cuts down on the need for trusted third parties to verify transactions.
In doing so, blockchain technology is giving people around the world access to fast, cheap, and borderless payments. Bitcoin transactions can take 30 minutes or up to 16 hours — in extreme cases — to settle.
The number of confirmed Bitcoin transactions per day has grown 8x from just over 50, in the summer of to more thanas of Meanwhile, as transaction fees can be high, developers are actively working on scaling cheaper solutions for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Other cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin Cash, already have low-priced transactions. Currently, transaction fees on Bitcoin Cash are hovering at around 20 cents per transaction. One company, TenX, is approaching the payments problem slightly differently.
The company is building a distributed network to trade between different cryptocurrencies and working to integrate that network with physical cards. While cryptocurrencies are a long way from completely replacing fiat when it comes to payments, the last couple of years have seen exponential growth in transaction volume for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In developing countries today, blockchain promises to give billions of people around the world access to financial services.
One example of this is BitPesaa blockchain company focused on facilitating B2B payments in countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and Uganda. Compared to a whopping 9. Over the past couple of years, BitPay, a payment processor for Bitcoin, has seen a sharp rise in transaction payment volume.
Another example is BitPaya Bitcoin payment service provider that helps merchants accept and store Bitcoin payments. One big reason behind the coming disruption of the payments industry is the fact that the creaky infrastructure supporting it is just as liable to disruption — the world of clearance and settlements. Download this report for a full explainer. The fact that an average bank transfer — as described above — takes three days to settle has a lot to do with the way our financial infrastructure was built.
Moving money around the world is a logistical nightmare for the banks themselves. Today, a simple bank transfer — from one account to another — has to bypass a complicated system of intermediaries, from correspondent banks to custodial services, before it ever reaches any kind of destination.
The two bank balances have to be reconciled across a global financial system, comprised of a wide network of traders, funds, asset managers and more. Each correspondent bank maintains different ledgers, at the originating bank and the receiving bank, which means that these different ledgers have to be reconciled at the end of the day. The actual money is then processed through a system of intermediaries.
That means that instead of having to rely on a network of custodial services and correspondent banks, transactions could be settled directly on the blockchain. That would help alleviate the high costs of maintaining a global network of correspondent banks. Ripple currently has over customers signed up to experiment with its blockchain network. Ripple and R3 seek to decentralize systems on a smaller scale than public blockchains by connecting financial institutions to the same ledger in order to increase efficiency of transactions.
Blockchain projects are doing more than just making existing processes more efficient, however. The fundraising space is perhaps the best example of this. Raising money through venture capital is an arduous process. Entrepreneurs put together decks, sit through countless meetings with partners, and endure long negotiations over equity and valuation in the hopes of exchanging some chunk of their company for a check. Anyone is free to raise money from anyone at any time, and anyone can invest in projects they find interesting.
On the blockchain, fundraising takes the form of an initial coin offering ICO. Projects sell tokens, or coins, in exchange for a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The value of the token is — at least in theory — tied to the success of its implementation in the future. Investing in tokens is a way for investors to bet directly on usage and value. Through ICOs, blockchain companies can short-circuit the conventional fundraising process by selling tokens directly to the public. First, ICOs occur globally and online, giving companies access to an exponentially larger pool of investors. Second, ICOs give companies immediate access to liquidity.
Compare that to ten years for venture-backed startups. Venture capital is taking notice, with VC firms like Sequoia, Andreessen Horowitz, and Union Square Ventures all directly investing in ICOs, as well as gaining exposure by investing in cryptocurrency hedge funds. And I hope it does. The democratization of everything is what has excited me about technology from the beginning.
With greater access to private capital and alternative fundraising methods such as ICOs, we can expect to see this profitable market for investment banks decline even further. Low interest rates and higher regulation have made private funding more attractive to many startups than the public markets. Telegram offers a free service with high user growth — but its lack of revenue makes it unlikely to succeed in the public markets.
The idea behind the ICO is to sell tokens to users and bootstrap a payment platform on top of the messaging network. If, as blockchain advocates predict, the next Facebook, Google, and Amazon are built around decentralized protocols and launched via ICO, it will eat directly into investment banking margins. Companies like CoinListwhich began as a collaboration between Protocol Labs and AngelList, are helping bring digital assets to the mainstream by helping blockchain companies structure legal and compliant ICOs.
It has developed a bank-grade compliance process that blockchain companies can access through a streamlined API, helping projects ensure everything from due diligence to investor accreditation. Investment banks today are experimenting with automation to help eliminate the thousands of work hours that go into an IPO. And CoinList is just the start.
A number of companies are emerging around the new ICO ecosystem, from Waves, a platform for storing, managing, and issuing digital assets, to Republic.
While the majority of ICOs thus far have been for pre-revenue blockchain projects, they have the potential to expand much further and become a viable alternative to traditional funding. To buy or sell assets like stocks, debt, and commodities, you need a way to keep track of who owns what. Financial markets today accomplish this through a complex chain of brokers, exchanges, central security depositories, clearing houses, and custodian banks. These different parties have been built around an outdated system of paper ownership.
Say you want to buy a share of Apple stock. You might place an order through a stock exchange, which matches you with a seller. So we outsource the shares to custodian banks for safekeeping. To settle and clear an order on an exchange involves multiple intermediaries and points of failure.
In practice, that means that when you buy or sell an asset, that order is relayed through a whole bunch of third parties. Transferring ownership is complicated because each party maintains their own version of the truth in a separate ledger.
Because there are so many different parties involved, transactions often have to be manually validated. Each party charges a fee. Blockchain technology promises to revolutionize financial markets by creating a decentralized database of unique, digital assets. While Bitcoin and Ethereum have accomplished this with purely digital assets, new blockchain companies are working on ways to tokenize real-world assets, from stocks to real estate to gold.
The potential for disruption is massive. While fees are typically lower than. Using the blockchain, tokenized securities have the potential to cut out middlemen such as custodian banks altogether, lowering asset exchange fees. Further, through smart contracts, tokenized securities can work as programmable equity — paying out dividends or performing stock buybacks through a couple lines of code.
Finally, putting real-world assets on the blockchain has the potential to usher in broader, global access to markets. Polymath is one of the blockchain companies that wants to help migrate trillions of dollars of financial securities to the blockchain.
Polymath is building a marketplace and platform that helps people issue security tokens, and implement governance mechanisms to help these new tokens meet regulations. The Australian Stock Exchange announced an effort to replace its system for bookkeeping, clearance, and settlements with a blockchain solution developed by Digital Asset Holdings.
While tokenized assets are a hugely promising use case for the blockchain, the biggest hurdle is regulatory. Regulatory and legislative guidance will be key to the success of these nascent projects. The worlds of the consumer, the financial institution, and blockchain are slowly converging.
Traditional banks and lenders underwrite loans based on an inaccurate and insecure system of credit reporting. They do this by looking at factors like your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and home ownership status.
To get this information, they have to access your credit report provided by one of three major credit agencies: Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. Based on that information, banks price the risk of a default into the fees and interest collected on loans. This centralized system is often hostile to consumers.