Paypal to bitcoin instant exchange
27 comments
Dogecoin solo mining gpu monitors
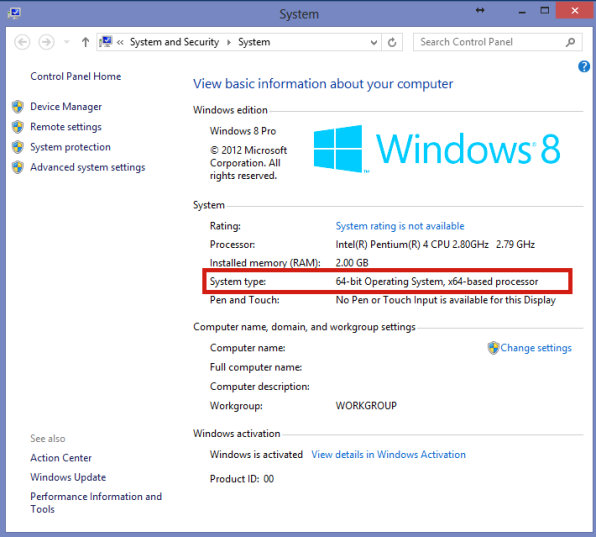
What's the difference between 32 bit OS and 64 bit OS? Can a 32 bit OS run in a 64 bit processor? Your question is architecture specific. It supports a 64 bit address space. It provides some new instructions and new registers. You can run bit x86 Windows on an x64 machine. Note that you can't do this on Itanium bit systems. A 64 bit processor can run both 32 and 64 OS at least an x64 can.
A 32 bit processor can run only 32 natively. Now if you look at current computers it is obvious why the world is moving to 64 bit: The CPU has more registers and thus allows more efficient code. On other architectures the differences between 64 and 32 bit are less obvious. For example the Nintendo 64 remember that?
So in that case 64 bit served more as a marketing trick. The currently-accepted answer is generally correct but not specifically so. In particular, it references the number of address selection lines between the CPU and the memory, i. In the days of yore when the CPU when people used to sit down and weave wrap the wires between a processor and the memory, you would have had to use either 32 or theoretically, because it didn't exist at the time 64 wires between the CPU and the memory controller that would be used to specify which memory address you wanted to access.
For example, let's say we have a 2-bit memory architecture: If you take a bit CPU and you add on 32 more wires between the CPU and the memory controller so that you're magically able to support more memory, you now have a "bit CPU" that can run bit code or bit code. What does this mean and how does this happen? Existing "2-byte" code will run, setting the values of the last 2 wires like indicated above We'll wire the extra connection to be zero by default, so actually when the 2-byte code runs, when it selects 00, it's actually selecting and when it selects 11 it's actually selecting Now a programmer wants to write "native" 3-byte code and writes her software to take advantage of the extra address space.
She tells the CPU that she knows what she's doing and that she'll take manual control of the new, extra wires. Her software knows about the extra wire s and correctly sends out , giving her full access to the range of memory supported by the this new CPU architecture. But that's not how it has to happen. In fact, that's normally not how things happen.
That was the story of the Intel Itanium, now famously known as the "Itanic" because of how massively it sank. It was supposed to herald in the new bit era, and it was something to behold. Variable length instructions, huge caches, bit address space, tons of registers, super exciting, super cool, and super hard to convince everyone to recompile or rewrite 20 years of legacy code for.
AMD came up with a winning strategy to get everyone to switch over to the bit world while preserving compatibility with bit applications, in a way that a bit OS could run on bit hardware or even bit applications could run on a bit OS on bit hardware. Both a 32 and 64 bit OS can run on a 64 bit processor, but the 64 bit OS can use full-power of the 64bit processor larger registers, more instructions - in short it can do more work in same time.
A 32 bit processor supports only 32 bit Windows OS. Thank you for your interest in this question. Because it has attracted low-quality or spam answers that had to be removed, posting an answer now requires 10 reputation on this site the association bonus does not count. Would you like to answer one of these unanswered questions instead?
Questions Tags Users Badges Unanswered. Super User is a question and answer site for computer enthusiasts and power users. Join them; it only takes a minute: Here's how it works: Anybody can ask a question Anybody can answer The best answers are voted up and rise to the top. The question seems more whether you can install say Win Vista x86 onto a box that have a bits processor, rather than whether x86 apps run on say Win Vista x Mehrdad Afshari 2, 4 20 Mahmoud Al-Qudsi 2, 3 20 You have a few factual errors: This is incorrect generally, though correct for x64 specifically.
A 32 bit processor will run any operating system designed to run on such a processor architecture. However you use false logic in your argument. Using your logic means, it is generally not correct that a 32 bit OS can run on a 32 bit processor. Stack Overflow for Teams is Now Available. Super User works best with JavaScript enabled.