R9 290a edfd litecoin exchange
48 comments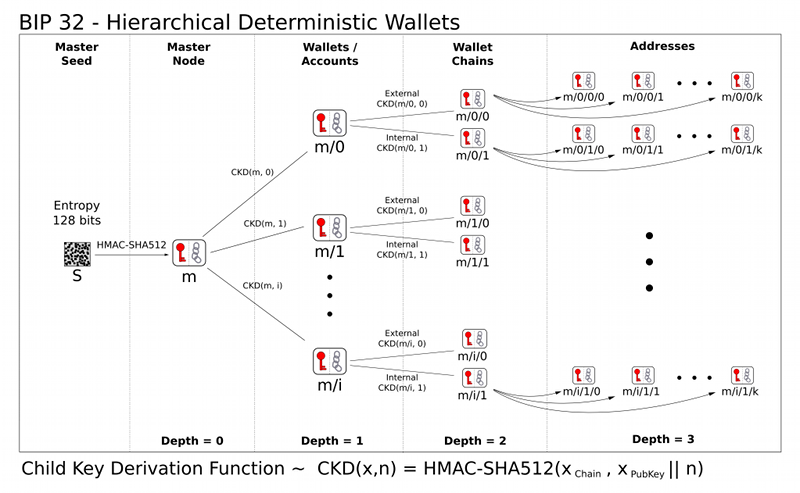
Feathercoin to bitcoin calculator value
This list is meant to focus your preparation, not provide an exhaustive list of all possible test materials. Understand what a centralized ledger is and how money has been organized on centralized ledgers in the modern digital economy.
Wake up little Suzie Future of blockchain Wat is macro-economy. How does money arise: It is a money system capital 'B' , 2. What is an altcoin. Bitcoins are like any other currency: The value of a bitcoin is constantly changing, and there is no centralised exchange for it. Think of it this way: There is no 'fixed' price. Usually, it's the seller's responsibility to give a fair price to the buyer based on what rate bitcoins are being traded in elsewhere. The difference between bitcoins and other currencies is that there is no centralised bank that prints the currency and sets relative values.
Through transactions, the value of bitcoin fluctuates through supply and demand. Understand the principles of asymmetric encryption and the impact it has on key exchange. Understand the relationship between digital signatures and asymmetric keys. Understand how users, advocates, developers, businesses, and governments impact the Bitcoin Protocol. Explain what types of institutions are actively involved in promoting, maintaining, or lobbying on behalf of the industry.
Explain the relationship between bitcoin addresses, public keys, and private keys; distinguish between them and describe the primary use of each. In terms of addresses and keys, describe how funds are accessed and transferred on the bitcoin network. Bitcoin Addresses and Keys.
Describe a bitcoin transaction in terms of inputs and outputs. Explain why a simple bitcoin transaction is irreversible. Understand the basics of transaction fees. What information is public? Know and understand the denominations of bitcoin and their relation to one another e. Explain the difference between Bitcoin capitalized B and bitcoin. Recognize other commonly used symbols referring to bitcoin as a digital currency. Understand network basics such as how the network is connected and the importance of independent nodes in the structure.
Explain common network attacks such as DDoS and how the network is secured from these types of attacks. What is a BIP? Explain the basic process of submitting, evaluating, and implementing a BIP. People wishing to submit BIPs, first should propose their idea or document to the mailing list.
After copy-editing and acceptance , it will be published here. We are fairly liberal with approving BIPs, and try not to be too involved in decision making on behalf of the community.
The exception is in very rare cases of dispute resolution when a decision is contentious and cannot be agreed upon. In those cases, the conservative option will always be preferred.
Having a BIP here does not make it a formally accepted standard until its status becomes Active. For a BIP to become Active requires the mutual consent of the community. Those proposing changes should consider that ultimately consent may rest with the consensus of the Bitcoin users see also: So the ability for a protocol change to be successfully implemented ultimately rests with those who accept bitcoins in exchange for value.
Generally those will be the merchants. If the economic majority doesn't run full nodes Bitcoin is dead. What is a bitcoin exchange? Who uses bitcoin exchanges and why? Understand the risks of storing bitcoin on exchanges and identify best practices for storing bitcoin.
What is a blockchain explorer? How can they be used to trace payments? What is an Unspent Transaction Output? How do these affect transactions you send and the change that is leftover from your transaction?
Why is this explanation wrong and why? Explain the basic value that miners provide to the bitcoin network. How are new bitcoins created? What is a mining pool? What is a centralized mining pool? What is a P2P pool? From the perspective of the network: From the perspective of a miner: What is the most popular hardware used today for bitcoin mining? Explain what a potential attacker can and cannot do with a large proportion of network hashing power.
Understand the relationship between mining pools, specialized hardware, and the likelihood of attacks. What is a bitcoin wallet and how are they used? The Hierarchical Deterministic HD key creation and transfer protocol BIP32 , which allows creating child keys from parent keys in a hierarchy. Wallets using the HD protocol are called HD wallets. An Oracle in this context is a trusted third party that signs transactions only when certain conditions are met, in order to enforce security or implement other functions.
HDM wallets with a third-party Oracle can provide security while not compromising usability. The user retains custody of 2 out of 3 keys, and does not experience counterparty risk, while still relying on a trustworthy third party to countersign normal transactions. The trusted third party, an Oracle, vets transactions to protect a user from theft, fraud and risk without being able to take possession or control of funds.
The Oracle can also alert the user to wallet compromise and merchants with negative reputation. For more about 2-of-3 multisignature wallets, please see BIP and the Storage white paper.
Describe the difference between lightweight and full clients. The Bitcoin reference client uses randomly generated keys. In order to avoid the necessity for a backup after every transaction , by default keys are cached in a pool of reserve keys. Still, these wallets are not intended to be shared and used on several systems simultaneously. They support hiding their private keys by using the wallet encrypt feature and not sharing the password, but such "neutered" wallets lose the power to generate public keys as well.
Deterministic wallets do not require such frequent backups, and elliptic curve mathematics permit schemes where one can calculate the public keys without revealing the private keys. This permits for example a webshop business to let its webserver generate fresh addresses public key hashes for each order or for each customer, without giving the webserver access to the corresponding private keys which are required for spending the received funds.
However, deterministic wallets typically consist of a single "chain" of keypairs. The fact that there is only one chain means that sharing a wallet happens on an all-or-nothing basis. However, in some cases one only wants some public keys to be shared and recoverable. In the example of a webshop, the webserver does not need access to all public keys of the merchant's wallet; only to those addresses which are used to receive customer's payments, and not for example the change addresses that are generated when the merchant spends money.
Hierarchical deterministic wallets allow such selective sharing by supporting multiple keypair chains, derived from a single root. The motivation to make this proposal stems from observations of the way physical bitcoins and paper wallets are used.
An issuer of physical bitcoins must be trustworthy and trusted. Even if trustworthy, users are rightful to be skeptical about a third party with theoretical access to take their funds. A physical bitcoin that cannot be compromised by its issuer is always more intrinsically valuable than one that can. A two-factor physical bitcoin solution is highly useful to individuals and organizations wishing to securely own bitcoins without any risk of electronic theft and without the responsibility of climbing the technological learning curve necessary to produce such an environment themselves.
Two-factor physical bitcoins allow a secure storage solution to be put in a box and sold on the open market, greatly enlarging the number of people who are able to securely store bitcoins. One of the most popular services provided by these payment processors is the instant conversion of Bitcoin BTC to your local fiat currency like USD for example. This is important for many businesses because most businesses which accept Bitcoin payments still have to pay all of their own costs and buy stock using fiat money, so changes in the exchange rate between Bitcoin and the businesses local currency could lead mogelijke klant in vroege aanbiedingsfase to losses if the BTC accepted as payment is not instantly converted into fiat.
Payment processors also provide you with all of the tools and reports that you need to make accepting Bitcoin payments as simple and convenient as possible without you having to develop your own software solution. What is the Secure Payment Protocol and how is it used on the network? How can you identify secure payments compared with standard payments?
This BIP describes a protocol for communication between a merchant and their customer, enabling both a better customer experience and better security against man-in-the-middle attacks on the payment process. Retrieved from " http: Navigation menu Personal tools Log in. Views Read View source View history. Navigation Main page Recent changes. This page was last modified on 20 November , at




