Adi shamir bitcoin exchange rate
44 comments
Build a bitcoin miner asic shoes
The tongue starts to develop at about 4 weeks. The tongue originates from the first, second, and third pharyngeal arches which induces the migration of muscles from the occipital myotomes.
A U-shaped sulcus develops in front of and on both sides of the oral part of the tongue. This allows the tongue to be free and highly mobile, except at the region of the lingual frenulum, where it remains attached. Disturbances during this stage cause tongue tie or ankyloglossia. During the sixth week of gestation, the medial nasal processes approach each other to form a single globular process that in time gives rise to the nasal tip, columella, prolabium, frenulum of the upper lip, and the primary palate.
During early gestation as early as 4 weeks the lingual frenulum serves as a guide for the forward growth of the tongue. After birth the tip of the tongue continues to elongate, giving the impression of the frenulum retracting, though in reality this has been going on for some time before birth.
This is what gives the impression that the frenulums of some previously tongue-tied infants will "stretch" with age and growth. Many others continue to cause problems throughout life, unless corrected. The thin strip of tissue that runs vertically from the floor of the mouth to the undersurface of the tongue is called the lingual frenulum. It tends to limit the movement of the tongue, and in some people, it is so short that it actually interferes with speaking.
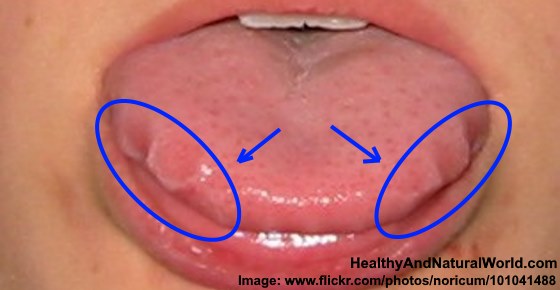
The base of the frenulum contains a "V" shaped hump of tissue in the floor of the mouth which houses a series of saliva gland ducts. The two largest ducts are in the center just in front of the attachment of the lingual frenulum and are called Wharton's Ducts.
They empty the submandibular submaxillary and sublingual salivary glands. These ducts can be quite active in some persons, and upon occasion, a considerable amount of saliva may erupt from them while talking, eating, yawning, or cleaning the teeth in a process known as gleeking.
The sublingual saliva glands empty through a series of tiny ducts in the tissue on either side of Wharton's ducts. The tongue is attached to the floor of the oral cavity by the frenulum. Superficial veins run through the base of the frenulum known as varicosities.
Their presence is normal, becoming more and more prominent as the patient ages. Ankyloglossia , also known as tongue-tie, is a congenital anomaly characterised by an abnormally short lingual frenulum; when severe, the tip of the tongue cannot be protruded beyond the lower incisor teeth. Additionally, an abnormally short frenulum in infants can be a cause of breastfeeding problems, including sore and damaged nipples and inadequate feedings.
Traumatic lesions on the ventral surface undersurface of the tongue, especially the lingual frenulum, can be caused by friction between the tongue and the mandibular central incisor teeth during cunnilingus and other oral sexual activities such as anilingus [10] [11] [12] [13] in what is sometimes known as cunnilingus tongue or cunnilingus syndrome. The condition manifests as pain and soreness on the undersurface of the tongue, [15] and sometimes the throat. Differential diagnosis is with other causes of oral ulceration such as aphthous stomatitis , secondary herpetic lesions, syphilis , etc.
Topical anesthetic may be used to relieve symptoms while the lesion heals. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Frenulum of tongue The mouth cavity.
The apex of the tongue is turned upward, and on the right side a superficial dissection of its under surface has been made. Frenulum labeled at center right.
Sagittal section of nose mouth, pharynx, and larynx. Frenulum linguae is topmost label at right. Clinical forensic medicine a physician's guide 3rd ed. Porter; Kursheed Moos; Jose Bagan Oral and maxillofacial diseases: Oral and maxillofacial diseases 3rd ed. Handbook of obstetric and gynecologic emergencies 4th ed. Color atlas of oral diseases 3rd ed. Anatomy of the mouth. Vermilion border Frenulum of lower lip Labial commissure of mouth Philtrum. Hard palate Soft palate Palatine raphe Incisive papilla.
Parotid gland duct Submandibular gland duct Sublingual gland duct. Oropharynx fauces Plica semilunaris of the fauces Uvula Palatoglossal arch Palatopharyngeal arch Tonsillar fossa Palatine tonsil. Breast pump Nipple shield Nursing bra Nursing chair Supplemental nursing system. Baby-led weaning Weaning Extended breastfeeding. Retrieved from " https: Pages with unresolved properties. Views Read Edit View history. In other projects Wikimedia Commons. This page was last edited on 11 February , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Anatomical terminology [ edit on Wikidata ].